
Fischer Black (1972) developed another version of CAPM, called Black CAPM or zero-beta CAPM, that does not assume the existence of a riskless asset. Sharpe, Markowitz and Merton Miller jointly received the 1990 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics for this contribution to the field of financial economics. Sharpe (1964), John Lintner (1965a,b) and Jan Mossin (1966) independently, building on the earlier work of Harry Markowitz on diversification and modern portfolio theory. The CAPM was introduced by Jack Treynor (1961, 1962), William F. Despite its failing numerous empirical tests, and the existence of more modern approaches to asset pricing and portfolio selection (such as arbitrage pricing theory and Merton's portfolio problem), the CAPM still remains popular due to its simplicity and utility in a variety of situations.
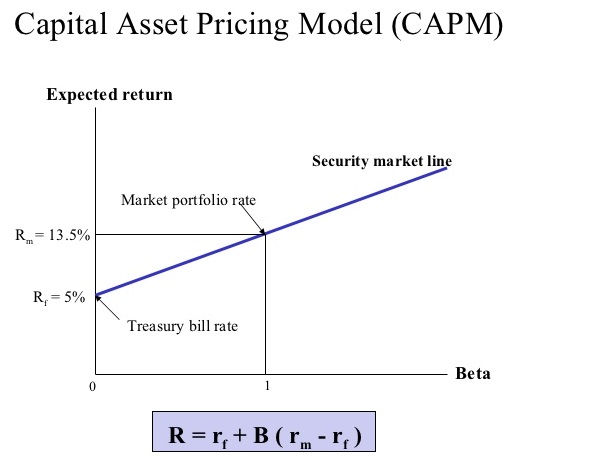
Under these conditions, CAPM shows that the cost of equity capital is determined only by beta. CAPM assumes a particular form of utility functions (in which only first and second moments matter, that is risk is measured by variance, for example a quadratic utility) or alternatively asset returns whose probability distributions are completely described by the first two moments (for example, the normal distribution) and zero transaction costs (necessary for diversification to get rid of all idiosyncratic risk). The model takes into account the asset's sensitivity to non-diversifiable risk (also known as systematic risk or market risk), often represented by the quantity beta (β) in the financial industry, as well as the expected return of the market and the expected return of a theoretical risk-free asset. In finance, the capital asset pricing model ( CAPM) is a model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, to make decisions about adding assets to a well-diversified portfolio. JSTOR ( April 2021) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message)Īn estimation of the CAPM and the security market line (purple) for the Dow Jones Industrial Average over 3 years for monthly data.Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.įind sources: "Capital asset pricing model" – news Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. By adding a portion of risk-free assets and borrowing the additional investments needed at a risk-free rate, the risk can be either decreased or increased.This article needs additional citations for verification. The risk-free asset leads to the curved efficient frontier of MPT and makes the linear efficient frontier of the CAPM simple.Īs a result, the investors would not concentrate on the qualities of individual assets. There is a risk-free asset and there is no restriction on borrowing and lending at the risk-free rateĬAPM assumes the availability of risk-free assets to simplify the complex and paired covariance of Markowitz’s theory.
In other words, it is difficult to draw a common efficient frontier line if the available information is not accessible to all. If some investors alone are able to have access to special information, that is limited to only some investors, then the markets are regarded inefficient.
Capital asset pricing model capm free#
One of the important assumptions is that all investors have free access to all the required and available information free of cost. Varying preferences also mean that the price of an asset will be different for different investors. Moreover, the efficient portfolio of each asset will be different from others. When the expectations differ, the anticipated mean and variance forecasts differ significantly.ĭue to this, innumerable efficient frontiers are possible. In other words, all investors’ anticipation of risk and returns are the same. The expectations of risk and return of all investors are the same.
Capital asset pricing model capm series#
CAPM provides a series of efficient frontlines because individuals have different perceptions towards risk and reward. Some investors use Beta only to measure the risk while others use both beta and variance of returns. There are differences among investors regarding the use of Beta. Only the systematic that varies with the Beta of the security remains. CAPM reinstates that rational investors discard their diversifiable risks or unsystematic risks.

The return and risk are calculated by the variance and the mean of the portfolio. Choice on the basis of risks and returnsĬAPM states that Investors make investment decisions based on risk and return. Diversification is needed to provide these investors more returns. Here are the five most influential assumptions of CAPM − The investors are risk-averseĬAPM deals with risk-averse investors who do not want to take the risk, yet want to earn the most from their portfolios. The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) has some assumptions upon which it is built.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
